Abuse of Ethereum feature results in $60 million theft from 99K individuals
Bad actors have been exploiting Ethereum's 'Create2' function to circumvent wallet security warnings and compromise cryptocurrency addresses. This activity resulted in the theft of cryptocurrency valued at $60,000,000 from 99,000 individuals over a six-month period.

Cybercriminals have exploited Ethereum's 'Create2' function to stealthily bypass wallet security warnings, leading to the theft of $60 million in cryptocurrency from nearly 99,000 victims over six months. This alarming trend was identified by Web3 anti-scam experts at 'Scam Sniffer', who documented several instances of this exploitation, with individual losses in some cases reaching as high as $1.6 million.
The 'Create2' opcode, a feature added to Ethereum in the 'Constantinople' upgrade, is intended for legitimate use, allowing the creation of smart contracts on the blockchain. Unlike its predecessor, the original Create opcode, Create2 enables the calculation of contract addresses before their deployment. This feature offers significant advantages for Ethereum developers, including more sophisticated and adaptable contract interactions, the ability to pre-calculate contract addresses based on parameters, greater deployment flexibility, and better alignment with off-chain transactions and specific decentralized applications (dApps).
However, the introduction of Create2 also brought unforeseen security risks and opened new avenues for attacks. According to Scam Sniffer's report, malicious actors are using Create2 to generate new contract addresses that have no prior record of suspicious or flagged transactions, effectively evading wallet security alerts. When an unsuspecting user signs a transaction with malicious intent, the attacker quickly deploys a contract to the pre-calculated address and diverts the victim's assets there, making the transaction irreversible.
One notable incident involved a victim losing $927,000 in GMX tokens. They were deceived into signing a contract that unknowingly transferred their assets to a pre-computed address controlled by the attacker. This misuse of Ethereum's Create2 function underscores the need for heightened awareness and enhanced security measures in the realm of cryptocurrency transactions.
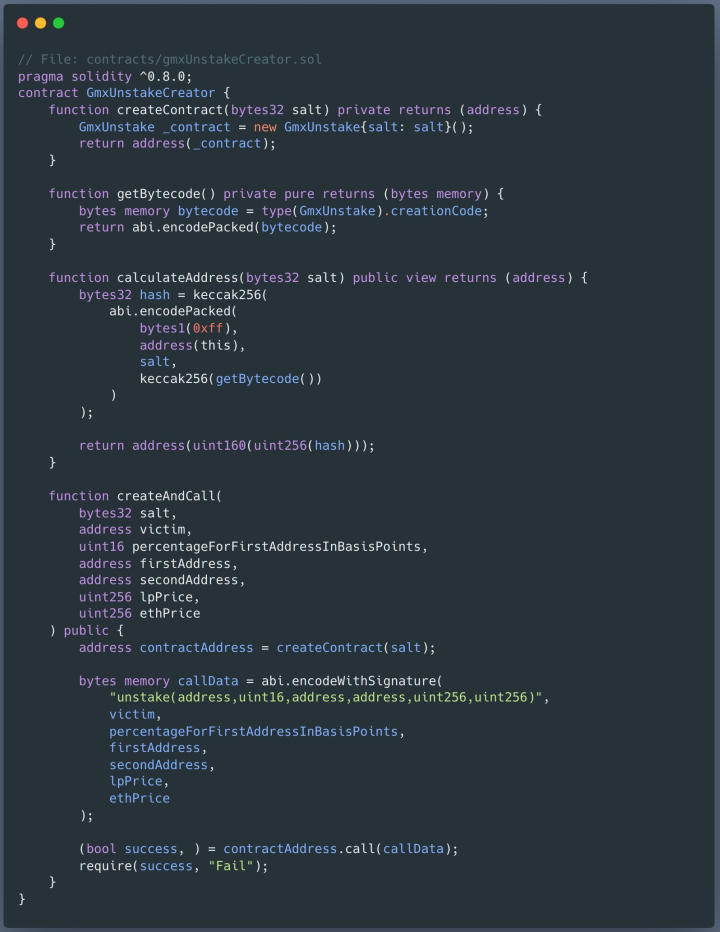
A sophisticated form of scam called 'address poisoning' has been increasingly used by cybercriminals to deceive cryptocurrency users. This technique exploits Ethereum's Create2 function to create addresses resembling legitimate ones owned by intended recipients. Scammers generate a vast number of addresses and select those closely matching their phishing targets, effectively tricking users into sending assets to the fraudsters under the impression they are transacting with familiar, trusted addresses.
Since August 2023, Scam Sniffer has documented 11 victims who collectively lost close to $3 million due to this scam, including one individual who transferred a staggering $1.6 million to an address they mistakenly believed was one they had previously transacted with.
These 'address poisoning' attacks, which subtly drain millions, have occasionally garnered attention within the crypto community. Earlier this year, MetaMask, a popular cryptocurrency wallet, issued warnings about scammers creating new addresses that closely resemble those a victim had recently used in transactions. In some instances, the attacker might even deposit a small amount of cryptocurrency to the victim's wallet, registering the fraudulent address in the wallet's history, thereby increasing the likelihood of the victim unknowingly sending a significant payment to the scammer.
In one notable incident from early August 2023, a Binance operator inadvertently sent $20 million to scammers using this 'address poisoning' technique. Fortunately, the error was quickly identified, and the recipient's address was frozen, preventing the loss of funds.
The effectiveness of such scams is further underscored by their similarity to tactics used in clipboard-hijacking malware, such as the Laplas Clipper, which also relies on substituting legitimate cryptocurrency addresses with fraudulent ones.
To safeguard against these deceptive practices, it is essential for individuals conducting cryptocurrency transactions to meticulously verify the recipient's address in its entirety, rather than relying solely on a cursory check of the first and last few characters. This careful approach is crucial for preventing substantial financial losses due to such sophisticated phishing scams.























![Largest Data Breaches in US History [Updated for 2023]](https://nulld3v.com/uploads/images/202311/image_430x256_654e69df8d469.jpg)












